The Effect of Bay Leaf (Syzygium polyanthum) Decoction on Lowering Blood Pressure in Hypertensive Patients
Keywords:
Bay Leaf, Blood Pressure, Chronic Disease, Herbal Therapy, HypertensionAbstract
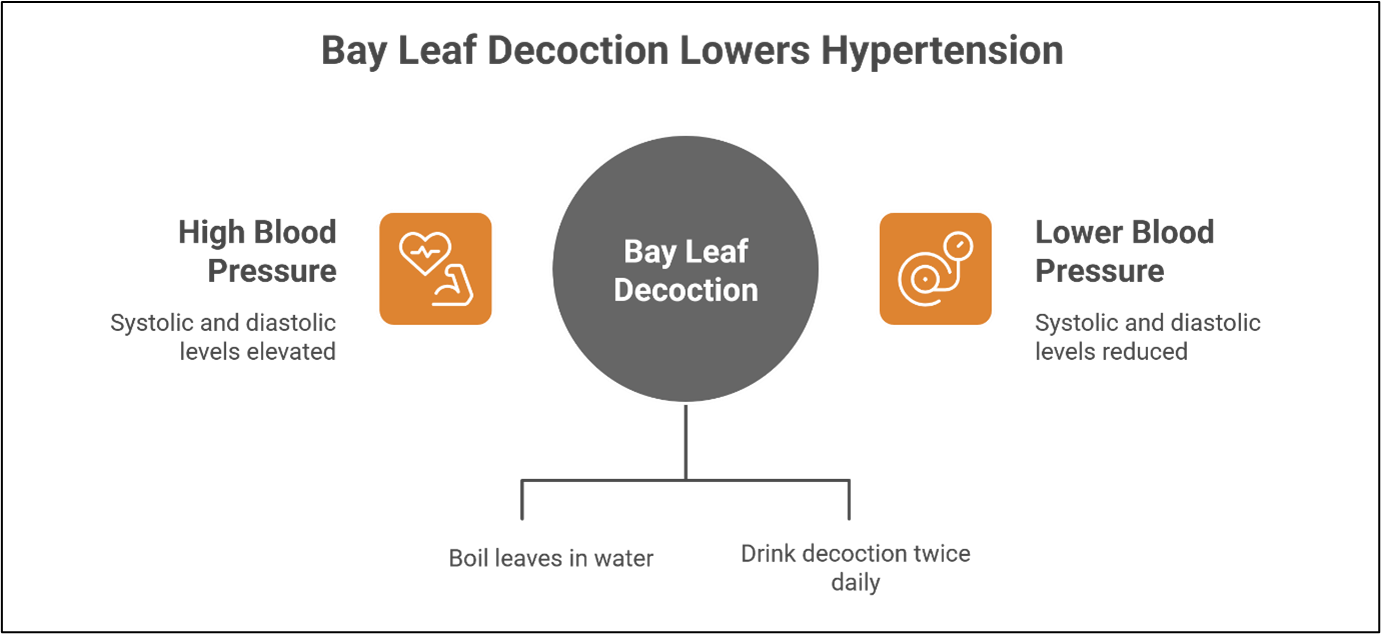
Hypertension is a chronic disease and a leading cause of global mortality, prompting interest in non-pharmacological therapies. This study aimed to investigate the effect of bay leaf (Syzygium polyanthum) decoction on blood pressure changes in patients with hypertension. This pre-experimental study employed a one-group pre-test-post-test design with 30 hypertensive patients at the Watubelah Public Health Center in Cirebon Regency. The intervention consisted of a decoction of 10 bay leaves boiled in 400 mL of water until 200 mL remained, which was consumed twice daily for seven days. Data were analyzed using the Wilcoxon test. The results showed a significant decrease in the mean systolic blood pressure from 153.6 mmHg to 138.4 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure from 93.8 mmHg to 84.1 mmHg (p = 0.001). This study concludes that bay leaf decoction is associated with a significant reduction in blood pressure in hypertensive patients, suggesting its potential as a complementary therapy in nursing practice.
Downloads
References
Mills KT, Stefanescu A, He J. The global epidemiology of hypertension. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020 Apr;16(4):223–37.
WHO. First WHO report details devastating impact of hypertension and ways to stop it [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2025 Oct 20]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news/item/19-09-2023-first-who-report-details-devastating-impact-of-hypertension-and-ways-to-stop-it
Kemenkes RI. Riset Kesehatan Dasar (Riskesdas). Jakarta: Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Kesehatan Kementerian Kesehatan RI; 2018.
Hapsari VA, Nasruddin H, Pancawati E. Relationship Between Lifestyle And Hypertension Incidence. Jurnal EduHealth. 2024 Dec 31;15(04):1318–25.
Mansoor K, Khan HW, Khattak MI, Imran M, Tahir HB, Zia Q. Comparison between the Efficacy of Amlodipine with Captopril in the Management of Uncontrolled Blood Pressure in the Emergency Department. Pakistan Armed Forces Medical Journal. 2022;72(6):2074–7.
Trisia T, Kurniawati D, Nastiti K, Aryzki S. Monitoring Efek Samping Obat Antihipertensi Di Puskesmas Kertak Hanyar Kabupaten Banjar. Journal Pharmaceutical Care and Sciences. 2025 June 30;5(2):198–208.
Rahmawati I, Kaswati L. Comparison of Phenolic Content of Indonesian Bay Leaves (Syzygium polyanthum) Fresh Decoction And Herbal Tea. Indonesian Journal of Pharmaceutical Science and Technology. 2023;5(2):140–5.
Soraya S. Testing the Tannin Content of Bay Leaves (Syzygium polyanthum) Using Various Ethanol Concentrations. Jurnal Skala Kesehatan. 2023 Sept 24;14(2):129–35.
Batool S, Khera RA, Hanif MA, Ayub MA. Bay Leaf. In: Medicinal Plants of South Asia [Internet]. Elsevier; 2020 [cited 2025 Oct 20]. p. 63–74. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/B9780081026595000057
Handayati A, Suhariyadi, Pestariati. Efforts to Control Blood Pressure for Prolanis Hypertension Members through the Utilization of Bay Leaf Decoction. Frontiers in Community Service and Empowerment [Internet]. 2025 Oct 10 [cited 2025 Oct 20];4(3). Available from: https://ficse.ijahst.org/index.php/ficse/article/view/104
Sukrasno S, Anggadiredja K, Dudi D, Suciatmo AB. Antihypertensive Effect of Bay Leaf Extract (Syzygium polyanthum (Wight) Walp., Myrtaceae). Acta Pharmaceutica Indonesia. 2013 Dec 30;38(4):134–8.
S I, Rosdianah R, Wahyuningsih TY, Yunus M. Decoction of bay leaf (syzygium polyanthum) against the reduction of high blood pressure in 3-month injectable birth control receptors. fulltext PDF. 2024 Dec 1;13(2):257–64.
Guerrero L, Castillo J, Quiñones M, Garcia-Vallvé S, Arola L, Pujadas G, et al. Inhibition of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Activity by Flavonoids: Structure-Activity Relationship Studies. PLoS One. 2012 Nov 21;7(11):e49493.
Ullagaddi R. Unveiling the Medicinal Properties of Bay Leaves: An Overview. International Journal of Research Publication and Reviews. 2025;6(7):4968–75.
Panjaitan RGP, Putri AD, Wahyuni ES, Ningsih K, Titin T, Fitriawan D, et al. Ethnobotanical study of antihypertensive medicinal plants in Sari Makmur Village, West Kalimantan, Indonesia. Biodiversitas Journal of Biological Diversity [Internet]. 2025 Aug 11 [cited 2025 Oct 20];26(7). Available from: https://smujo.id/biodiv/article/view/21957
Eryta E. Efek Daun Salam (Syzygium Polyanthum) dan Seledri (Apium Graveolens) Terhadap Hipertensi. Termometer: Jurnal Ilmiah Ilmu Kesehatan dan Kedokteran. 2025 Feb 25;3(2):41–6.
Sari Pratiwi D, Armayani A, Yati M, Poddar R. The effect of Bay Leaf Decoction on reducing Blood pressure in Hypertension patients in The working area of South Lasalimu. RJPT. 2024 Jan 19;169–71.
Bachri MochS, Putranti W, Widiyastuti L, Devie RS. Ethanol extract combinations effect of celery herb (Apium graveolens L.) and bay leaf (Syzygium polyanthum W.) toward hypertensive mice induced by sodium chloride and high fat feed. AMR. 2021 Apr;1162:151–8.
Grassi D, Desideri G, Ferri C. Flavonoids: Antioxidants Against Atherosclerosis. Nutrients. 2010 Aug 12;2(8):889–902.
Cao Y, Xie L, Liu K, Liang Y, Dai X, Wang X, et al. The antihypertensive potential of flavonoids from Chinese Herbal Medicine: A review. Pharmacol Res. 2021 Dec;174:105919.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Ahmad Syaripudin

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- Ahmad Syaripudin, Spiritual Well-Being, Self-Care, and Quality of Life in Indonesian Patients with Coronary Heart Disease: A Correlational Study in a Regional Hospital of Cirebon, Indonesia , Journal of Health and Nutrition Research: Vol. 4 No. 2 (2025)


















