Correlation between Platelet Indices and PELOD-2 Score as Prognostic Markers in Pediatric Sepsis at Dr. Zainoel Abidin Hospital
Keywords:
Children, Mean Platelet Volume, PELOD-2, Platelet Distribution Width, SepsisAbstract
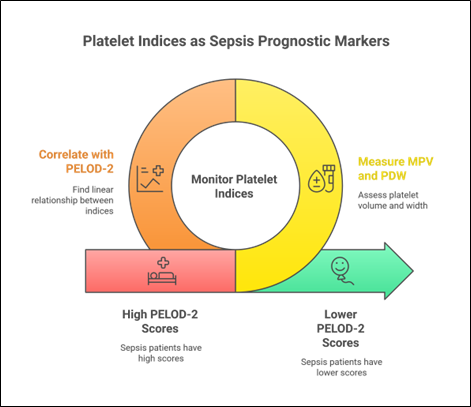
To determine the correlation between Mean Platelet Volume (MPV) and Platelet Distribution Width (PDW) with Pediatric Logistic Organ Dysfunction (PELOD-2) scores as prognostic markers in pediatric sepsis. This prospective cohort study included 44 pediatric sepsis patients admitted to the PICU at Dr. Zainoel Abidin Hospital from July to September 2024. PELOD-2 scores and blood indices were assessed on admission (Day 1) and Day 3. Pearson correlation was used to analyze the relationship between variables. The majority of patients were female (59.1%) and under one year old (31.8%). By Day 3, 68.2% of patients exhibited MPV levels exceeding 10.4 fL. Significant moderate correlations were found between Day 3 MPV and PELOD-2 (r=0.410; p=0.006), Day 3 PDW and PELOD-2 (r=0.518; p=0.001), and the changes ($\Delta$) in PDW versus PELOD-2 scores (r=0.471; p=0.005). Increases in MPV and PDW are significantly correlated with PELOD-2 scores, suggesting their potential utility as accessible prognostic markers in pediatric sepsis management.
Downloads
References
Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia. KMK tentang Pedoman Nasional Pelayanan Kedokteran Tatalaksana Sepsis Pada Anak [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 June 19]. Available from: https://yankes.kemkes.go.id/unduhan/fileunduhan_1610419769_850165.pdf
Wulandari A, Martuti S, Kaswadi P. Perkembangan diagnosis sepsis pada anak. Sari Pediatri. 2018;19(4):237.
Weiss SL, Fitzgerald JC, Maffei FA, Kane JM, Rodriguez-Nunez A, Hsing DD, et al. Discordant identification of pediatric severe sepsis by research and clinical definitions in the SPROUT international point prevalence study. Critical care (London, England). 2015 Sept;19(1):325.
Plunkett A, Tong J. Sepsis in children. BMJ (Clinical research ed). 2015 June;350:h3017.
Lee IR, Shin J Il, Park SJ, Oh JY, Kim JH. Mean platelet volume in young children with urinary tract infection. Scientific Reports. 2015;5(June):1–6.
Han X, Xu P, Duan X, Liu Y, Zhang J, Xu H. High mean platelet volume-to-platelet count ratio as a diagnostic maker for increased risk of liver function damage in pediatric patients with infectious mononucleosis in China. Experimental and therapeutic medicine. 2019 Dec;18(6):4523–7.
Mangalesh S, Dudani S, Malik A. Platelet Indices and Their Kinetics Predict Mortality in Patients of Sepsis. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2021 Oct;37(4):600–8.
Lestari RP, Sumadiono S, Arguni E. An increase in mean platelet volume (MPV) as a predictor of mortality in children with sepsis. Journal of the Medical Sciences (Berkala Ilmu Kedokteran) [Internet]. 2022 Apr 20 [cited 2025 Nov 17];54(1). Available from: https://jurnal.ugm.ac.id/bik/article/view/69057
Setiawan PA, Wati DK, Suparyatha IBG, Hartawan INB, Sidiartha IGL, Pratiwi IGAPE. The Association of PELOD-2 Score and Nutritional Status of Children Treated in the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit at Prof. Dr. I.G.N.G. Ngoerah Hospital Denpasar, 2020-2022. Intisari Sains Medis. 2024 June 14;15(2):642–5.
Korniluk A, Koper-Lenkiewicz OM, Kamińska J, Kemona H, Dymicka-Piekarska V. Mean Platelet Volume (MPV): New Perspectives for an Old Marker in the Course and Prognosis of Inflammatory Conditions. Mediators Inflamm. 2019 Apr 17;2019:9213074.
Yuniar I, Karyanti MR, Kurniati N, Handayani D. The clinical and biomarker approach to predict sepsis mortality in pediatric patients. Paediatrica Indonesiana. 2023 Mar 6;63(1):37–44.
Sovira N, Ismi J, Trisnawati Y, Lubis M, Yusuf S. Profil Penyakit Kritis di Ruang Rawat Intensif Anak RSUD Dr. Zainoel Abidin Banda Aceh. Sari Pediatri. 2020 Aug 28;22(2):92–7.
Sayed SZ, Mahmoud MM, Moness HM, Mousa SO. Admission platelet count and indices as predictors of outcome in children with severe Sepsis: a prospective hospital-based study. BMC Pediatr. 2020 Aug 19;20(1):387.
Pairunan JN, Runtunuwu AL, Salendu PM. Hubungan pemeriksaan hitung darah lengkap pada anak dengan sepsis. e-CliniC. 2016;4(1):76–81.
Salim H, B SI, Nym BHI. Penggunaan Skor Pediatric Logistic Organ Dysfunction Harian sebagai Prediktor Mortalitas Anak yang Dirawat di Unit Perawatan Intensif Anak. Sari Pediatri. 2016 Nov 9;16(2):141–6.
İşgüder R, Ceylan G, Ağın H, Nacaroğlu HT, Korkmaz HA, Devrim İ, et al. Increased mean platelet volume in children with sepsis as a predictor of mortality. Turk J Pediatr. 2016;58(5):503–11.
Miraza A, Buana B, Evalina R, Siregar J, Amalia C Saragih R, Lubis S. Correlation of Neutrophil Lymphocyte Ratio and Monocyte Lymphocyte Ratio to The Pelod-2 Score In Critically Ill Children. IJRP. 2023 Dec 16;140(1):506–14.
Gao Y, Li Y, Yu X, Guo S, Ji X, Sun T, et al. The Impact of Various Platelet Indices as Prognostic Markers of Septic Shock. PLOS ONE. 2014 Aug 13;9(8):e103761.
Amri I, Rahma R, Hutasoit GA, Putri ASD, Harun H, Rasyid R. Comparison of Neutrophile-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Between Dengue Haemorrhagic Fever and Dengue Shock Syndrome in Pediatric Patients at Anutapura Hospital. Journal of Health and Nutrition Research. 2025 Apr 24;4(1):162–71.
Putri ASD, Supriono S, Tonowidjojo VD, Fitriani J, Utama GN, Muthmainah AA, et al. Evaluation of C-Reactive Protein, Neutrophil-To-Lymphocyte Ratio, and Absolute Neutrophil Count as Simple Diagnostic Markers for Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis. Journal of Health and Nutrition Research. 2025 Aug 1;4(2):815–21.
Vagdatli E, Gounari E, Lazaridou E, Katsibourlia E, Tsikopoulou F, Labrianou I. Platelet distribution width: a simple, practical and specific marker of activation of coagulation. Hippokratia. 2010 Jan;14(1):28–32.
Tsompos C, Panoulis C, Toutouzas K, Zografos G, Papalois A. The Effect of the Antioxidant Drug “U-74389G” on Creatinine Levels during Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in Rats. Curr Urol. 2016 May;9(2):73–8.
Nabilah K, Muhdar IN, Lestari WA, Sariman S. The Relationship Between Macro-Nutrient Intake, Food Security, and Nutrition-Related Knowledge with The Incidence of Stunting in Toddlers. J Health Nutr Res. 2024 Aug 26;3(2):164–71.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Sari Novita Pratiwi, Nora Sovira, Eka Destianti Edward, Heru Noviat Herdata, Mulya Safri, Jufitriani Ismy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.


















