Lifestyle Behaviors and Risk of Metabolic Syndrome: A Case-Control Study among Fishermen and Oil Palm Farmers
Keywords:
Behavioral Risk Factors, Coffee Consumption, Fishermen, Health-Seeking Behavior, Metabolic SyndromeAbstract
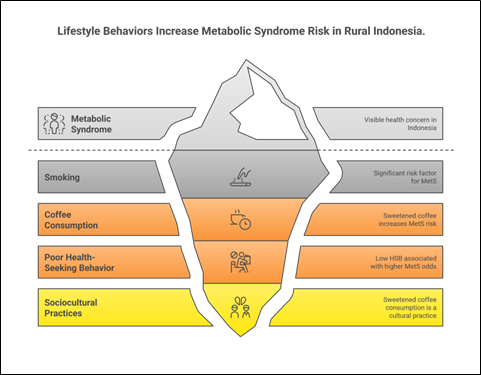
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is a growing health concern in Indonesia, particularly in rural communities with limited healthcare access. Behavioral risk factors such as smoking, coffee consumption, and poor health-seeking behavior (HSB) may increase MetS risk in vulnerable populations. This study aimed to examine the association between lifestyle behaviors—smoking, coffee consumption, and HSB—and the risk of MetS among fishermen and oil palm farmers in Aceh, Indonesia. A case-control study was conducted among 240 adults, comprising 120 couples, recruited from rural fishing and farming communities. Cases met the IDF 2020 MetS criteria, while controls did not. Data on sociodemographics, smoking, coffee intake, and HSB were collected via structured interviews and clinical assessments. Multivariate logistic regression was used to identify independent risk factors, adjusting for age, gender, and education. Smoking among husbands (AOR = 2.89; 95% CI: 1.19–7.02; p = 0.019), coffee consumption (AOR = 2.40; 95% CI: 1.00–5.79; p = 0.049), and low HSB (AOR = 3.10; 95% CI: 1.35–7.11; p = 0.008) were significantly associated with higher odds of MetS. While age and education were not independently significant, they were retained in the model as potential confounders. This study highlights the need for tailored health promotion targeting smoking cessation, improved health service engagement, and dietary awareness in rural Indonesian populations. Interventions should consider sociocultural practices such as sweetened coffee consumption to reduce MetS risk effectively.
Downloads
References
Cota ESLA, Gouvea TM, Fernandes FC, Carrillo MRGG, Veloso VM, Santos Filho AF, et al. Yoga practice can reduce metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular risk in climacteric women. J Behav Med [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2023 Jun 14]; Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10865-023-00420-y
Alberti KGMM, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ, Cleeman JI, Donato KA, et al. Harmonizing the Metabolic Syndrome: A Joint Interim Statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation. 2009 Oct 20;120(16):1640–5.
Kemenkes. Hasil Riset Kesehatan Dasar [Internet]. Jakarta: Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Kesehatan, Kementerian Kesehatan RI; 2018. Available from: https://www.litbang.kemkes.go.id
Lasmadasari N, Pardosi M. Studi Prevalensi Dan Faktor Risiko Sindrom Metabolik Pada Nelayan Di Kelurahan Malabro Bengkulu. Media Kesehatan Masyarakat Indonesia. 2016. Vol. 12: Iss. 2, Article 4. DOI: 10.30597/mkmi.v12i2.926 .
Ephraim RKD, Owusu VB, Asiamah J, Mills A, Abaka-Yawson A, Kpene GE, et al. Predicting type 2 diabetes mellitus among fishermen in Cape Coast: a comparison between the FINDRISC score and the metabolic syndrome. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2020 Dec;19(2):1317–24.
Cremonini ACP, Ferreira JRS, Martins CA, Do Prado CB, Petarli GB, Cattafesta M, et al. Metabolic Syndrome and Associated Factors in Farmers in Southeastern Brazil: A Cross-Sectional Study. IJERPH. 2023 Jul 8;20(14):6328.
Nizmah N, Reski S, Wahyunigrum DR, Cahyono J. The Relationship of Balanced Nutrition Knowledge with the Attitudes and Behaviors of Young Women. J Health Nutr Res. 2024 Apr 10;3(1):91–8.
Nabilah K, Muhdar IN, Lestari WA, Sariman S. The Relationship Between Macro-Nutrient Intake, Food Security, and Nutrition-Related Knowledge with The Incidence of Stunting in Toddlers. J Health Nutr Res. 2024 Aug 26;3(2):164–71.
Taufik T, Novaria AA, Utami RP, Wiryanto W. The Relationship of Physical Activity, Energy, and Protein Intake with Nutritional Status in Adolescents at Junior High School. J Health Nutr Res. 2024 Apr 9;3(1):46–52.
Pickett W, King N, Lawson J, Dosman JA, Trask C, Brison RJ, et al. Farmers, mechanized work, and links to obesity. Preventive Medicine. 2015 Jan;70:59–63.
Rahim FF, Abdulrahman SA, Kader Maideen SF, Rashid A. Prevalence and factors associated with prediabetes and diabetes in fishing communities in penang, Malaysia: A cross-sectional study. Musinguzi G, editor. PLoS ONE. 2020 Feb 10;15(2):e0228570.
Berentzen NE, Beulens JW, Hoevenaar-Blom MP, Kampman E, Bueno-de-Mesquita HB, Romaguera-Bosch D, et al. Adherence to the WHO’s Healthy Diet Indicator and Overall Cancer Risk in the EPIC-NL Cohort. Gorlova OY, editor. PLoS ONE. 2013 Aug 7;8(8):e70535.
IDF. The IDF consensus worldwide definition of the metabolic syndrome. 2020.
Chiolero A, Faeh D, Paccaud F, Cornuz J. Consequences of smoking for body weight, body fat distribution, and insulin resistance. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2008 Apr;87(4):801–9.
Campagna D, Alamo A, Di Pino A, Russo C, Calogero AE, Purrello F, et al. Correction: Smoking and diabetes: dangerous liaisons and confusing relationships. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2023 Jun 2;15(1):117.
Azarpazhooh MR, Andalibi MSS, Hackam DG, Spence JD. Interaction of smoking, hyperhomocysteinemia, and metabolic syndrome with carotid atherosclerosis: A cross-sectional study in 972 non-diabetic patients. Nutrition. 2020 Nov;79–80:110874.
Bull FC, Al-Ansari SS, Biddle S, Borodulin K, Buman MP, Cardon G, et al. World Health Organization 2020 guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. Br J Sports Med. 2020 Dec;54(24):1451–62.
Cui GH, Li SJ, Yin YT, Chen LJ, Li JQ, Liang FY, et al. The relationship among social capital, eHealth literacy and health behaviours in Chinese elderly people: a cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health. 2021 Dec;21(1):45.
Tan YR, Jawahir S, Doss JG. Oral healthcare seeking behavior of Malaysian adults in urban and rural areas: findings from the National Health and Morbidity Survey 2019. BMC Oral Health. 2023 Oct 5;23(1):719.
O’Keefe JH, Bhatti SK, Patil HR, DiNicolantonio JJ, Lucan SC, Lavie CJ. Effects of Habitual Coffee Consumption on Cardiometabolic Disease, Cardiovascular Health, and All-Cause Mortality. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2013 Sep;62(12):1043–51.
Chung J, Choi HM, Jung JH, Kong MG. Association between Socioeconomic Status and Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Adults: Data from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Cardiometab Syndr J. 2021;1(2):168.
Park JH, Moon JH, Kim HJ, Kong MH, Oh YH. Sedentary Lifestyle: Overview of Updated Evidence of Potential Health Risks. Korean J Fam Med. 2020 Nov 20;41(6):365–73.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Besti Verawati, Hadi Riyadi, Ali Khomsan, Ikeu Ekayanti

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- Nur Laily Ramdhani, Cesilia Meti Dwiriani, Ali Khomsan , Determinants of Iron Supplementation Compliance Among Adolescent Girls in Kuningan Regency, Indonesia , Journal of Health and Nutrition Research: Vol. 4 No. 3 (2025)
- Maya Klementina Dasmasela, Hardinsyah Hardinsyah, Mira Dewi, Ikeu Ekayanti, Indrayana Indrayana, Local Food-Based Supplementation and Behavior Change Communication Improve Mid-Upper Arm Circumference (MUAC) in Pregnant Women: A Community-Based Intervention Study , Journal of Health and Nutrition Research: Vol. 4 No. 3 (2025)


















