The Impact of Body Composition on Wound Healing in Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Systematic Review
Keywords:
Body composition, Obesity, Sarcopenia, Type 2 diabetes mellitus, Wound healingAbstract
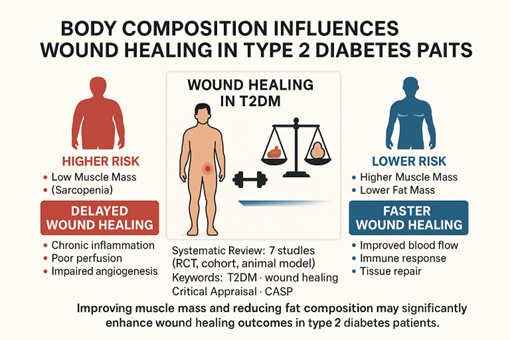
Wound healing in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) presents a major clinical challenge, particularly due to alterations in body composition such as reduced muscle mass and increased fat mass. This systematic review aimed to synthesize current evidence regarding the impact of body composition on wound healing effectiveness in T2DM patients. Literature was retrieved from PubMed, ProQuest, Wiley Online Library, and Google Scholar, targeting observational and experimental studies published between 2015 and 2025. Keywords included "type 2 diabetes mellitus", "wound healing", "body composition", "sarcopenia", and "obesity". Articles were selected based on predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Methodological quality was assessed using the Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP) checklist. A total of seven eligible studies were included and analyzed narratively. The findings from the 4 articles analyzed showed that low muscle mass (sarcopenia) and high fat mass (obesity) were associated with delayed wound healing in T2DM patients. Some studies indicate that patients with better body composition balance, such as higher muscle mass index, experience faster wound healing. Heterogeneity in measurement methods and study populations limits the strength of these conclusions. This review supports the hypothesis that body composition significantly influences wound healing outcomes in T2DM. Muscle mass reduction may impair tissue repair by limiting perfusion and immune responses, while increased fat mass may contribute to chronic inflammation that hinders tissue regeneration. Further longitudinal research with standardized assessments is needed. Interventions that promote muscle mass gain and fat mass control may be essential components in wound management strategies for diabetic patients.
Downloads
References
Goyal R JI. Diabetes Mellitus Type 2. StatPearls Internet. 2022;
Spampinato SF, Caruso GI, De Pasquale R, Sortino MA, Merlo S. The Treatment of Impaired Wound Healing in Diabetes: Looking among Old Drugs. Pharm Basel Switz. April 2020;13(4).
Burgess JL, Wyant WA, Abdo Abujamra B, Kirsner RS, Jozic I. Diabetic Wound-Healing Science. Med Kaunas Lith. Oktober 2021;57(10).
Patel S, Srivastava S, Singh MR, Singh D. Mechanistic insight into diabetic wounds: Pathogenesis, molecular targets and treatment strategies to pace wound healing. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;112:108615.
Mieczkowski M, Mrozikiewicz-Rakowska B, Kowara M, Kleibert M, Czupryniak L. The Problem of Wound Healing in Diabetes—From Molecular Pathways to the Design of an Animal Model. Vol. 23, International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022.
Wang X, Yuan CX, Xu B, Yu Z. Diabetic foot ulcers: Classification, risk factors and management. World J Diabetes. 2022;13(12):1049–65.
Zhao J, Yang S, Shu B, Chen L, Yang R, Xu Y, dkk. Transient High Glucose Causes Persistent Vascular Dysfunction and Delayed Wound Healing by the DNMT1-Mediated Ang-1/NF-κB Pathway. J Invest Dermatol. 2021;141(6):1573–84.
Ansari P, Akther S, Khan JT, Islam SS, Masud MdSR, Rahman A, dkk. Hyperglycaemia-Linked Diabetic Foot Complications and Their Management Using Conventional and Alternative Therapies. Vol. 12, Applied Sciences. 2022.
Widaningsih I, Ibrahim K, Nursiswati N. Factors Affecting Vascular Complications in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Literature Review. J Health Nutr Res. 24 April 2025;4(1):186–99.
Lim KP, Nasruddin AB, Md Rani N. The Effect of Individualised Glycemic Intervention on Wound Healing Rate in Diabetic Foot Ulcer (The EIGIFU Study). J ASEAN Fed Endocr Soc. 3 April 2018;33(1 SE-Original Articles):22.
Wiratama RD, Abdul Muhith, Hotimah Masdan Salim, Siti Nur Hasina. Analysis Of The Effect Of Hyperbarics On Reducing Blood Sugar And Wound Healing Phase In DM Patients : Systematic Review. J Qual Public Health. 27 November 2024;8(1 SE-Articles):22–32.
Lee SH, Kim SH, Kim KB, Kim HS, Lee YK. Factors Influencing Wound Healing in Diabetic Foot Patients. Vol. 60, Medicina. 2024.
Pérez MFG, Macías JES, Cantú AG, Garza-Silva A, Sánchez MÁS, Romero-Ibarguengoitia ME. A cross-sectional study to determinate the relationship between body composition & neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc Diabetol – Endocrinol Rep. 2025;11(1):4.
Fenner-Pena N, Fajardo VC, Froes L, Carvalho PAM, Comim FV, Sahade V, dkk. Phase angle and body composition in long-term type 1 diabetes in adults: a comparative study in a Brazilian public reference outpatient clinic. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024;16(1):269.
Lim JY, Kim E. The Role of Organokines in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes and Their Functions as Molecular Transducers of Nutrition and Exercise. Metabolites. 2023;13(9).
Younes S. The role of micronutrients on the treatment of diabetes. Hum Nutr Metab. 2024;35:200238.
Perry BD, Caldow MK, Brennan-Speranza TC, Sbaraglia M, Jerums G, Garnham A, dkk. Muscle atrophy in patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: roles of inflammatory pathways, physical activity and exercise. Exerc Immunol Rev. 2016;22:94–109.
Lopez-Pedrosa JM, Camprubi-Robles M, Guzman-Rolo G, Lopez-Gonzalez A, Garcia-Almeida JM, Sanz-Paris A, dkk. The Vicious Cycle of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Skeletal Muscle Atrophy: Clinical, Biochemical, and Nutritional Bases. Vol. 16, Nutrients. 2024.
Li Y. Causes And Treatment for Obesity: How to Solve Obesity in Singapore? Highlights Sci Eng Technol. Desember 2024;123:163–71.
Song L, Lou J, Liu X. Study on Body Composition of Patients with Diabetes Mellitus by Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry: A Morphological Study. Int J Morphol. 2024;42(2):261–9.
Solanki JD, Makwana AH, Mehta HB, Gokhale PA, Shah CJ. Body Composition in Type 2 Diabetes: Change in Quality and not Just Quantity that Matters. Int J Prev Med. 2015;6:122.
Al-Sofiani ME, Ganji SS, Kalyani RR. Body composition changes in diabetes and aging. J Diabetes Complications. Juni 2019;33(6):451–9.
Ly L, Vo KL, Cruel AC, Shubrook JH. Dermatological Manifestations of Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications. Diabetology. 2025;6(3):1–18.
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, dkk. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. Maret 2021;372:n71.
Eriksen MB, Frandsen TF. The impact of patient, intervention, comparison, outcome (PICO) as a search strategy tool on literature search quality: a systematic review. J Med Libr Assoc JMLA. Oktober 2018;106(4):420–31.
Basiri R, Spicer MT, Ledermann T, Arjmandi BH. Effects of Nutrition Intervention on Blood Glucose, Body Composition, and Phase Angle in Obese and Overweight Patients with Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Nutrients. 2022;14(17).
Schanuel FS, Romana‐Souza B, Monte‐Alto‐Costa A. Short‐Term Administration of a High‐Fat Diet Impairs Wound Repair in Mice. Lipids. 2020;55(1):23–33.
Mashili F, Joachim A, Aboud S, McHembe M, Chiwanga F, Addo J, dkk. Prospective exploration of the effect of adiposity and associated microbial factors on healing and progression of diabetic foot ulcers in Tanzania: Study protocol of a longitudinal cohort study. BMJ Open. 2019;9(12):1–9.
Sun Y, Song L, Zhang Y, Wang H, Dong X. Adipose stem cells from type 2 diabetic mice exhibit therapeutic potential in wound healing. Stem Cell Res Ther. Juli 2020;11(1):298.
Xia W, Liu Y, Jiang X, Li M, zheng S, Hou M, dkk. Lean Adipose Tissue Macrophage Derived Exosome Confers Immunoregulation to Improve Wound Healing in Diabetes. 2022.
Lin CL, Yu NC, Wu HC, Lee YY, Lin WC, Chiu IY, dkk. Association of Body Composition with Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Chart Review Study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. April 2021;18(9).
Kim SM, Kim YH, Jun YJ, Yoo G, Rhie JW. The effect of diabetes on the wound healing potential of adipose-tissue derived stem cells. Int Wound J. 2016;13:33–41.
Critical Apraisal Programme (CASP). Critical Appraisal Skills Programme. 2018;
CEBM The Oxford. Center for Evidence-Based Management (CEBMa). 2014;
O’Connor AM, Sargeant JM. Critical appraisal of studies using laboratory animal models. ILAR J. 2014;55(3):405–17.
Jeremy Howick, Iain Chalmers, Paul Glasziou, Trish Greenhalgh, Carl Heneghan, Alessandro Liberati, dkk. OCEBM Levels of Evidence [Internet]. 2011 [dikutip 4 Juli 2025]. Tersedia pada: https://www.cebm.ox.ac.uk/resources/levels-of-evidence/ocebm-levels-of-evidence
Burns PB, Rohrich RJ, Chung KC. The levels of evidence and their role in evidence-based medicine. Plast Reconstr Surg. Juli 2011;128(1):305–10.
Dawi J, Tumanyan K, Tomas K, Misakyan Y, Gargaloyan A, Gonzalez E, dkk. Diabetic Foot Ulcers : Pathophysiology , Immune Dysregulation , and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies. 2025;1–17.
Shridharani S, Wang H, Sacks J. Pressure Sores. Eplasty. Januari 2013;13:ic15.
Maffetone PB, Rivera-Dominguez I, Laursen PB. Overfat Adults and Children in Developed Countries: The Public Health Importance of Identifying Excess Body Fat. Front Public Health. 2017;5(July):1–11.
Saritessa N, Ibrahim K, Haroen H. Booklet-Based Education in Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Scoping Review. J Health Nutr Res. 24 April 2025;4(1):172–85.
Oktavia L, Astriana W, Akbar MA. The Effect of Peer Teaching Education on Diabetes Self-Care in Patients with Gestational Diabetes: A Quasi-Experimental Study. J Health Nutr Res. 27 April 2025;4(1):266–72.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Andi Sulfikar, Mulyati Mulyati, Hasni Hasni, Rusli Taher, Sartika Lukman, Muhammadong Muhammadong, Rindani Claurita Tobang, Indah Restika BN

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- Junaiddin Junaiddin, Baktianita Ratna Etnis, Muhamad Faizal Arianto, Exaudian Flourens Lerebulan, Andirwana Andirwana, Andi Sulfikar, Angelich Windy R Agung, Mulyati Mulyati, Astuti R, Hemoglobin Levels in the First and Third Trimesters of Pregnancy: A Comparison between Indigenous Papuan and Non-Indigenous Papuan Women , Journal of Health and Nutrition Research: Vol. 4 No. 2 (2025)


















